Video Moment Retrieval
It demonstrates state-of-the-art VMR performance through experimental validation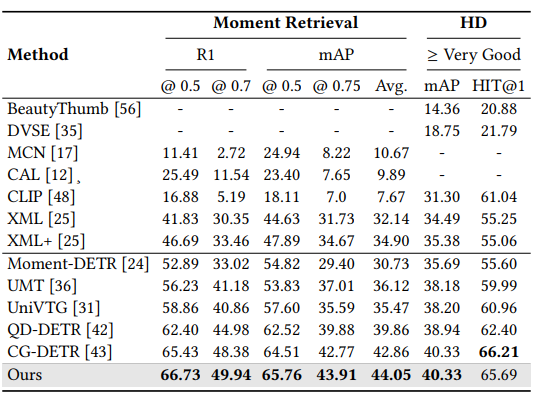
Results of joint moment retrieval and highlight de-tection (HD) on QVHighlights test split
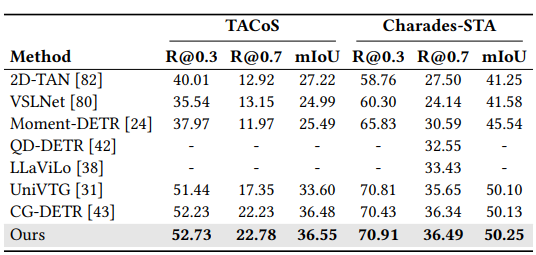
Moment retrieval results tested on TACoS and Charades-STA datasets
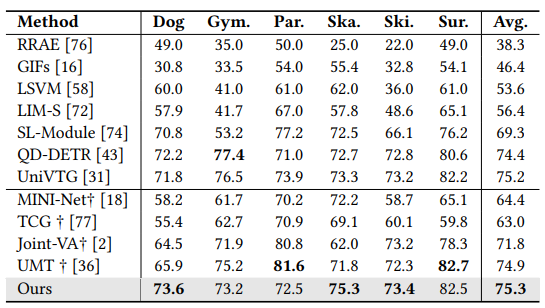
Performance of mAP for highlight detection on YouTube-HL
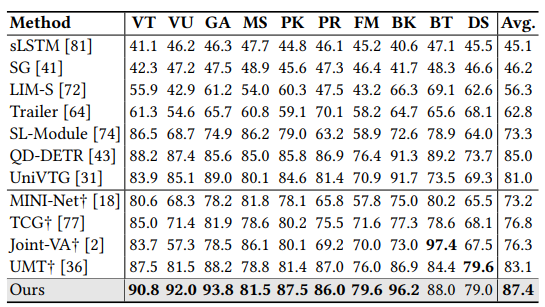
Highlight detection results on TV-Sum
To demonstrate the process of relation refinement in the VMR task, we break down each query into individual concepts and utilize them as separate queries for VMR. We visualize the model’s attention maps, showcasing its focus on both single-concept queries and the original queries (composed of combined concepts). It is evident that with the LLM encoder, the model has demonstrated a better understanding on the composition of the concepts
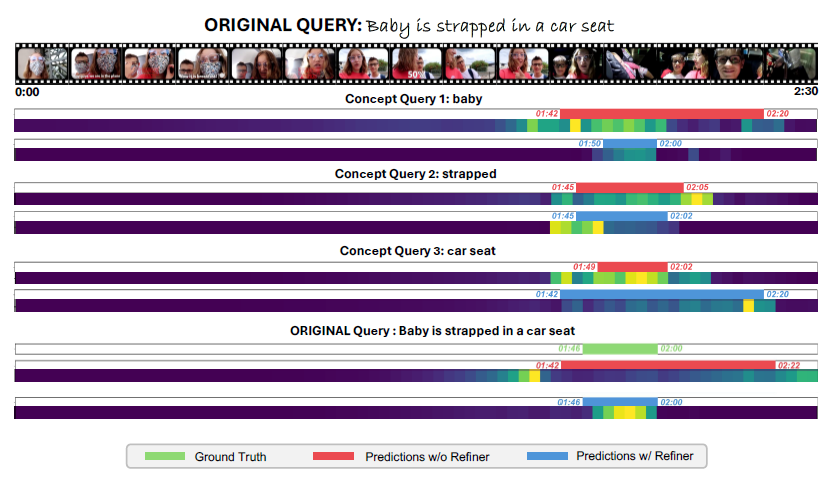
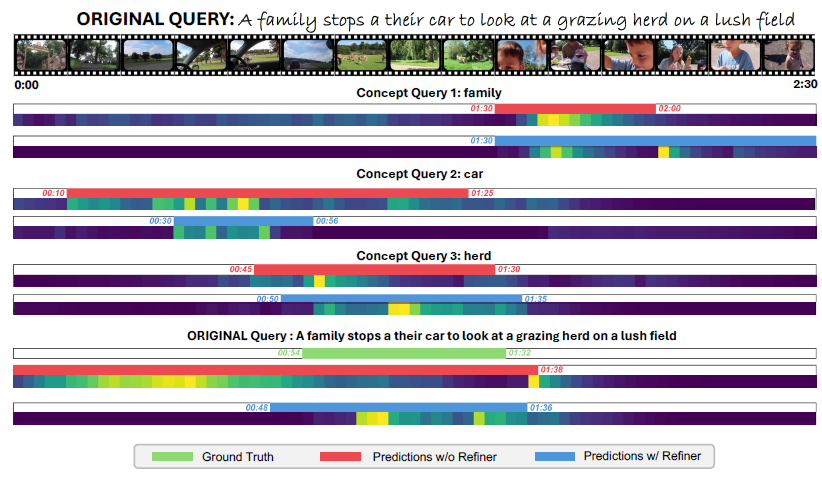
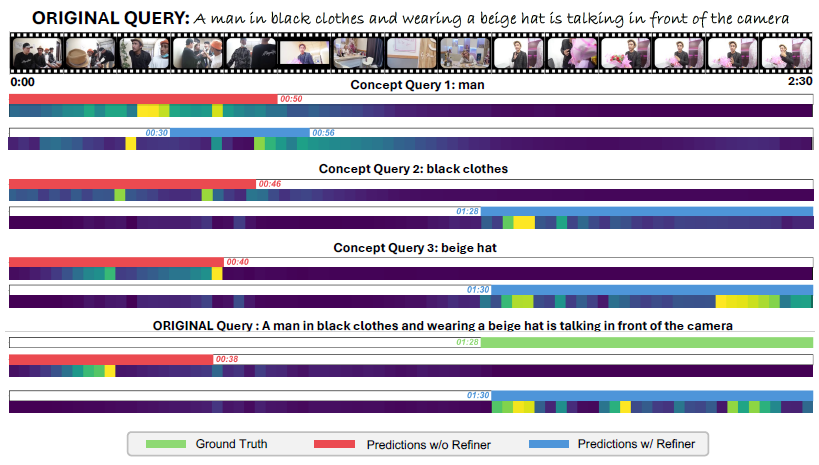
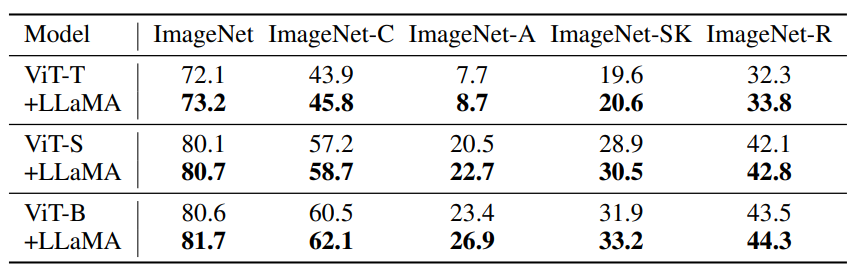
Image classification
Experiments on ImageNet and its variants (ImageNet-C, ImageNet-A, ImageNet-SK, ImageNet-R) using ViT models demonstrate that adding a single transformer block from LLaMA significantly enhances both accuracy and robustness.
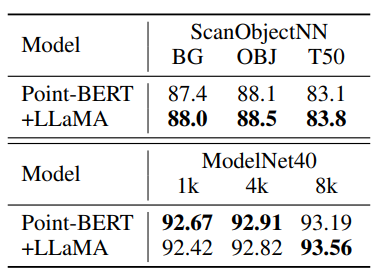
Point Cloud Classification
In 3D point cloud classification, adding the LLaMA transformer after the final attention block of the Point-BERT model improves accuracy on ScanObjectNN and ModelNet40 datasets, validating the applicability of LLM transformers across different modalities.
Action Recognition
Applying the pre-trained LLaMA transformer block in video action recognition, specifically on the SSv2 dataset, shows advantages in multi-frame video understanding, enhancing the accuracy of ViT-S and ViT-B models. 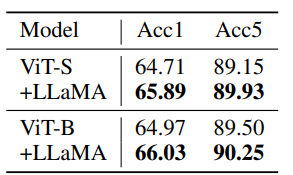
Motion Forecasting
In motion forecasting tasks, incorporating the LLaMA transformer in VectorNet and mmTransformer models improves trajectory predictions on the Argoverse dataset. Though the improvement is less pronounced compared to semantic tasks, it demonstrates potential in dynamic information understanding. 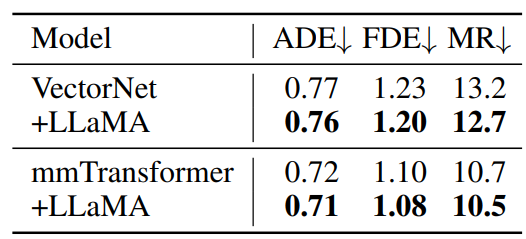
2D and 3D Visual Question Answering (VQA)
The LLaMA transformer is also applied to 2D and 3D visual-language tasks, including VQAv2 and SQA3D datasets. By integrating the LLaMA block after visual-language fusion, the models show enhanced question-answering capabilities and improved multimodal understanding.
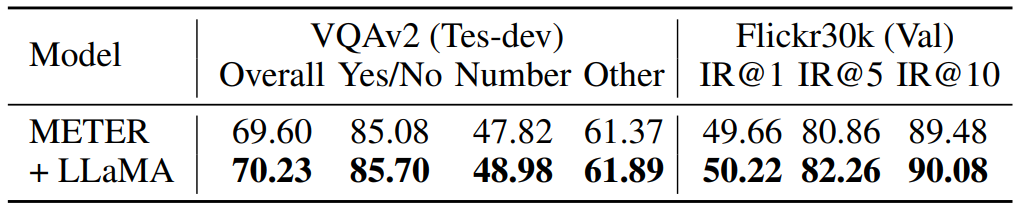
2D VQA and Image Retrieval
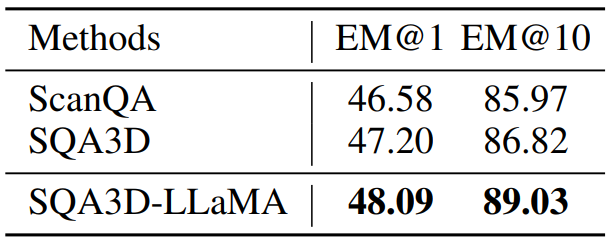
3D VQA
BibTeX
@inproceedings{
jiang2024prior,
title={Prior Knowledge Integration via {LLM} Encoding and Pseudo Event Regulation for Video Moment Retrieval},
author={Yiyang Jiang and Wengyu Zhang and Xulu Zhang and Xiaoyong Wei and Chang Wen Chen and Qing Li},
booktitle={ACM Multimedia 2024},
year={2024},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.15051}
}